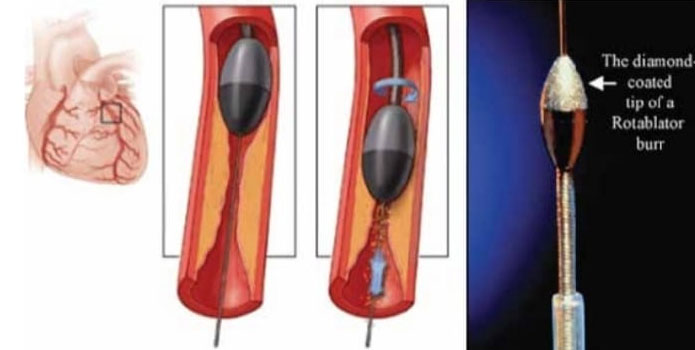
Rotablation is a specialized technique used in cardiology to treat severely calcified coronary artery lesions. It involves the use of a tiny, diamond-tipped burr mounted on a high-speed rotational device to gently remove the hardened plaque from the inner lining of the blood vessels.
Rotablation allows for precise and controlled removal of the calcified plaque, improving the vessel’s ability to expand and restore proper blood flow. After rotablation, additional treatments such as balloon angioplasty or stent placement may be performed to further optimize the blood flow in the treated artery.